Whether you're safeguarding your home against water damage, ensuring effective sewage management, or tackling large-scale drainage endeavors, this glossary serves as a guide. Explore the intricacies of backflow prevention, benchmarking elevations, or understanding the nuances of wastewater management. Empower yourself with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of drainage, enhancing the efficiency and longevity of your projects.
Backflow
Backflow refers to the unwanted reverse flow of water in a drainage system. In roofing, backflow can occur when water travels backward through downspouts, potentially causing damage.
Benchmark
A benchmark is a reference point used in drainage design to measure elevations. In homebuilding, benchmarks help establish the proper slope for effective water drainage away from structures.
Bolt-to-Bolt
Bolt-to-Bolt is a term used to ensure proper alignment and connection of drainage components. In HVAC, it ensures that bolts connecting ductwork remain tightly secured to prevent leaks.
Boot
A boot is a flexible connector used to join pipes in a drainage system. In homebuilding, boots are commonly used in plumbing and roof drainage systems to prevent water infiltration.
Catch Basin
A catch basin is a drainage structure designed to collect and redirect surface water. In roofing, catch basins prevent water pooling on flat surfaces and facilitate proper runoff.

Cavitation
Cavitation occurs when air bubbles in flowing water collapse, causing damage to drainage structures. In HVAC, cavitation may affect pumps and reduce efficiency.
Chicken Wire
Chicken wire is used in drainage projects to reinforce soil and prevent erosion. In landscaping, it helps stabilize the soil around drainage structures.
Chute (or Drop Chute, or Rock Chute)
A chute is a sloped structure designed to control the flow of water. In stormwater management, chutes are used to direct water away from vulnerable areas during heavy rain.
Collection Box
A collection box is a chamber that gathers water from multiple drains. In homebuilding, it helps consolidate water runoff from various roof sections.
Combined Sewer
A combined sewer system carries both stormwater and wastewater in a single pipe. In urban planning, addressing combined sewers is crucial for effective drainage.
Contour Line
A contour line represents a specific elevation on a topographic map. In landscaping, understanding contour lines aids in designing drainage systems that follow the natural slope of the land.
Cornice Drain
A cornice drain directs water away from building cornices to prevent damage. In roofing, proper cornice drains protect structures from water-related issues.
County Surveyor
A county surveyor oversees land surveys, including drainage assessments. In construction, collaboration with a county surveyor ensures compliance with local drainage regulations.
Cross-Section
A cross-section is a view of the terrain's vertical profile. In drainage design, cross-sections help visualize how water will flow through different elevations.
Culverts
Culverts are structures that convey water beneath roads or embankments. In civil engineering, culverts are essential for managing water flow in drainage systems.
Cut-and-Fill
Cut-and-fill is a construction method involving excavation and redistribution of soil. In drainage projects, cut-and-fill techniques shape the terrain for optimal water runoff.
Design Standards
Design standards are guidelines that dictate the parameters for drainage system planning. In homebuilding, adherence to design standards ensures effective water management.
Design Storm
A design storm represents a specific rainfall pattern used to assess drainage system capacity. In construction, planning for a design storm helps prevent flooding and water damage.
Detention
Detention refers to temporarily holding water to control its release. In stormwater management, detention basins slow down water flow, reducing the risk of flooding.
Discharge
Discharge is the volume of water released from a drainage system. In HVAC, discharge refers to the flow of air from ducts or vents.
Dome Strainer
A dome strainer is a protective device in drainage systems, featuring a domed shape with perforations to prevent debris from entering pipes. In roofing, dome strainers are commonly used in scupper drains, ensuring effective water flow while filtering out leaves and debris. In homebuilding, they play a crucial role in preventing clogs and maintaining efficient drainage.
Downspout
A downspout is a vertical pipe that directs water from a roof to the ground. In roofing, downspouts are crucial for efficient rainwater drainage.
Downspout Nozzle
A downspout nozzle is an attachment that directs water away from a building's foundation. In homebuilding, it prevents water accumulation near the structure.
Drain
A drain is a structure or conduit that removes excess water. In plumbing, drains remove wastewater from fixtures, while in landscaping, surface drains prevent water pooling.
Drain Dome
A drain dome is a protective cover for drainage openings. In roofing, drain domes prevent debris from clogging the drainage system.
Drain Grates
Drain grates are covers or gratings placed over openings in drainage systems to filter debris and prevent blockages. In roofing, drain grates are vital components in scupper drains or roof drains, allowing water to flow while keeping out leaves and debris. In homebuilding, they are essential for ground-level drainage, ensuring efficient water removal while preventing obstructions.
Drain Ring
A drain ring secures and supports a drain. In homebuilding, it ensures proper installation and stability of drain components.
Drainage
Drainage refers to the removal of excess water from an area. In construction, effective drainage prevents water-related damage to structures.
Drainage Board
A drainage board is a panel that facilitates water drainage in building foundations. In home construction, drainage boards protect basements from water infiltration.
Drainage Shed
A drainage shed is an area that contributes runoff to a specific drainage point. In urban planning, understanding drainage sheds helps manage stormwater effectively.
Drainage-way
A drainage-way is a natural or artificial channel for water flow. In landscaping, drainage-ways prevent soil erosion and direct water away from vulnerable areas.
Erosion
Erosion is the gradual loss of soil due to water, wind, or other environmental factors. In landscaping, erosion control measures are essential for maintaining a stable terrain.
Evaporation
Evaporation is the process of converting water into vapor. In drainage, understanding evaporation rates helps estimate water loss from retention or detention basins.
Filter Strip
A filter strip is a vegetated area that filters pollutants from surface runoff. In landscaping, filter strips improve water quality and prevent contamination.
Flap gate
A flap gate is a one-way valve that allows water to flow in only one direction. In stormwater management, flap gates prevent backflow and flooding during heavy rain.
Flap-gate
A flap-gate is a one-way valve used in drainage systems to regulate water flow. In civil engineering, flap-gates prevent water backup in sewers.
Floodplain
A floodplain is an area prone to flooding during heavy rainfall. In urban planning, avoiding construction in floodplains is crucial for preventing water damage.
Foundation Drain
A foundation drain is a system that directs water away from a building's foundation. In homebuilding, proper foundation drains prevent water infiltration and damage.
French drain
A French drain is a trench filled with gravel or rock that redirects surface water. In landscaping, French drains prevent water accumulation around structures.

Gradation
Gradation refers to the distribution of particle sizes in soil or aggregate. In construction, understanding gradation aids in selecting materials for effective drainage systems.
Grade
Grade is the slope or incline of the terrain. In drainage design, achieving the proper grade ensures efficient water runoff.
Gravel Stop
A gravel stop is a raised edge that prevents gravel or ballast from migrating. In roofing, gravel stops protect drainage systems and contribute to roof stability.
House Sewer
A house sewer is a pipe that carries wastewater from a building to the main sewer line. In plumbing, house sewers connect fixtures to the municipal sewer system.
Hydrograph
A hydrograph is a graph depicting the flow of water over time. In drainage design, hydrographs help assess the capacity of drainage systems during storms.
Impervious
Impervious surfaces do not absorb water. In landscaping, impervious materials contribute to increased surface runoff and may require specialized drainage solutions.
Infiltration
Infiltration is the process of water soaking into the ground. In drainage design, promoting infiltration helps manage surface water and prevent runoff.
Inflow
Inflow is the entry of water into a drainage system. In stormwater management, controlling inflow is crucial for preventing flooding and erosion.
Inlet
An inlet is an opening through which water enters a drainage system. In landscaping, inlets collect surface runoff for proper disposal.
Invert
The invert is the lowest point inside a drainage structure. In construction, understanding the invert is essential for designing effective drainage systems.
Kitchen drain
A kitchen drain removes wastewater from kitchen fixtures. In plumbing, kitchen drains connect sinks and appliances to the sewer or septic system.
Land Surveyor
A land surveyor measures and maps the terrain, identifying features relevant to drainage. In construction, land surveyors ensure accurate elevation data for drainage planning.
Model
A model is a representation of a drainage system used for analysis or simulation. In civil engineering, models help assess the performance of drainage designs.
Network
A drainage network is a interconnected system of pipes and structures. In urban planning, networks efficiently manage stormwater runoff in developed areas.
Open Drain
An open drain is a channel without a cover, allowing water to flow freely. In landscaping, open drains prevent water accumulation in low-lying areas.
Orifice
An orifice is an opening through which water flows in a drainage system. In stormwater management, orifices regulate water discharge and prevent flooding.
Outlet Channel
An outlet channel directs water away from a drainage system. In landscaping, outlet channels prevent water accumulation in low-lying areas.
Overflow
Overflow occurs when a drainage system surpasses its capacity, leading to excess water. In stormwater management, preventing overflow is crucial for avoiding flooding.
Parapet Sleeve
A parapet sleeve protects drains on building parapets. In roofing, parapet sleeves prevent water infiltration and contribute to overall drainage efficiency.
Peak Discharge
Peak discharge is the highest flow rate in a drainage system during a storm. In drainage design, understanding peak discharge helps size drainage components.
Percolation
Percolation is the movement of water through soil. In drainage design, percolation rates help assess the suitability of soil for managing stormwater.
Perennial Stream
A perennial stream flows continuously throughout the year. In hydrology, perennial streams contribute to drainage systems, carrying water to larger bodies.
Pop-up valve
A pop-up valve is a drainage component that opens to release water during storms. In landscaping, pop-up valves prevent waterlogging in low-lying areas.
Private Drain
A private drain is a drainage system serving a specific property. In homebuilding, private drains manage surface water from roofs and landscapes.
Reservoir
A reservoir stores water temporarily. In drainage design, reservoirs help regulate water flow, preventing flooding during heavy rainfall.
Retrofit Drains
Retrofit drains are drainage systems designed to upgrade or modify existing structures. In roofing, retrofit drains may be added to improve water drainage on older buildings. In homebuilding, retrofit drains can be installed to enhance the efficiency of existing drainage systems, addressing evolving needs and preventing water-related issues.
Runoff
Runoff is the flow of water over the ground surface. In landscaping, managing runoff is crucial for preventing erosion and directing water away from structures.
Saturation
Saturation occurs when soil reaches its maximum water-holding capacity. In drainage design, avoiding saturation helps maintain soil stability and prevent erosion.
Scupper Drain (or Parapet Drain)
A scupper drain is an opening in a wall or parapet for water drainage. In roofing, scupper drains prevent water accumulation on flat surfaces.
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the settling of particles in water. In stormwater management, sedimentation basins remove debris and pollutants from runoff.
Septic tank
A septic tank is a wastewater treatment system for individual properties. In plumbing, septic tanks separate solids from wastewater before disposal.
Sewage
Sewage is wastewater containing human waste and household effluent. In plumbing, sewage systems transport waste to treatment plants for proper disposal.
Sewer
A sewer is a pipe that carries wastewater from buildings to treatment facilities. In urban planning, sewers are essential for efficient drainage in developed areas.
Silt Fence
A silt fence is a barrier that prevents soil erosion and sediment runoff. In construction, silt fences protect water bodies from pollution during drainage projects.
Snaking
Snaking is the process of using a flexible tool to clear obstructions in drainage pipes. In plumbing, snaking removes clogs and ensures proper water flow.
Soffit
A soffit is the underside of a building's eaves. In roofing, soffits contribute to proper attic ventilation and prevent moisture buildup.
Storm drain
A storm drain is a structure that collects and conveys stormwater. In urban planning, storm drains prevent flooding by efficiently managing surface runoff.
Storm Sewer
A storm sewer is a system that carries stormwater away from developed areas. In construction, storm sewers prevent waterlogging and protect infrastructure.
Storm tanks
Storm tanks temporarily store stormwater before controlled release. In drainage design, storm tanks manage peak discharge and prevent flooding.
Stormwater Runoff
Stormwater runoff is the flow of water over surfaces during storms. In landscaping, managing stormwater runoff is crucial for preventing erosion and flooding.
Sub-House Drain
A sub-house drain collects and directs water away from a building's foundation. In homebuilding, sub-house drains protect structures from water-related damage.
Subsurface Drain (SSD)
A subsurface drain is a system below ground that collects and redirects water. In landscaping, SSDs prevent water accumulation around structures.
Sump pump
A sump pump removes water from basements or crawl spaces. In homebuilding, sump pumps prevent water damage by directing excess water away from foundations.
Sump Receiver (or Deckplate)
A sump receiver collects water from a drainage system. In roofing, sump receivers prevent water accumulation on flat roofs.
Surface Runoff
Surface runoff is water that flows over the ground surface. In drainage design, managing surface runoff prevents soil erosion and flooding.
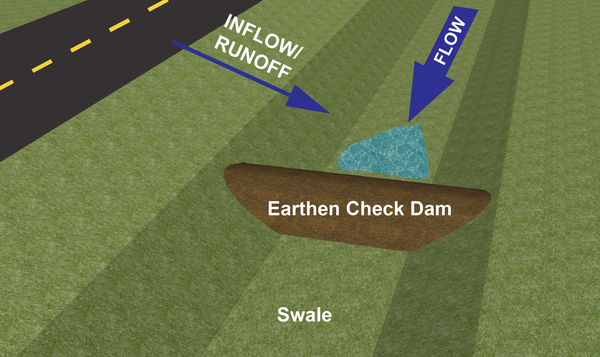
Swale
A swale is a shallow, vegetated channel that manages surface water. In landscaping, swales enhance drainage by directing water away from vulnerable areas.
Tile Drain
A tile drain is a buried pipe that collects and transports water. In agriculture, tile drains manage excess water, preventing waterlogged soil.
Tile Drainage
Tile drainage is a system of buried pipes that removes excess water from soil. In farming, tile drainage improves soil conditions for crop growth.
Toe of Slope
The toe of slope is the bottom point of a terrain incline. In construction, understanding the toe of slope helps plan drainage systems for efficient water flow.
Trap
A trap is a U-shaped pipe that prevents sewer gases from entering buildings. In plumbing, traps maintain a water seal to block odors from the sewer system.
Trash Rack
A trash rack is a barrier that prevents debris from entering a drainage system. In stormwater management, trash racks protect pipes and culverts from clogging.
Underdeck Clamp
An underdeck clamp secures drainage components beneath a structure. In construction, underdeck clamps prevent dislodgment and ensure system integrity.
Vent Piping
Vent piping facilitates the release of gases from plumbing systems, preventing pressure buildup. In roofing, vent pipes extend through the roof to promote proper ventilation; in homebuilding, they ensure efficient drainage and prevent sewer odors.
Wastewater
Wastewater refers to used water containing contaminants. In drainage, effective management of wastewater is essential to prevent environmental pollution, a concern in both residential and large-scale construction projects.
Water Table
The water table is the level at which the ground is saturated with water. In drainage, understanding the water table is crucial for designing effective systems, impacting foundation drainage in homebuilding and landscape drainage in roofing projects.
Watershed
A watershed is an area where water drains into a common outlet. In drainage planning, considering the watershed is vital for managing stormwater runoff, relevant in both residential and larger-scale drainage projects.

